Bio-Inspired Artificial Muscle-Tendon Complex of Liquid Crystal Elastomer for Bidirectional Afferent-Efferent Signaling
- Journal
- Advanced Materials
- Year
- 2025
- File
- Advanced Materials - 2025 - Cho - Bio‐Inspired Artificial Muscle‐Tendon Complex of Liquid Crystal Elastomer for.pdf (3.7M) 0회 다운로드 DATE : 2025-09-01 11:51:53
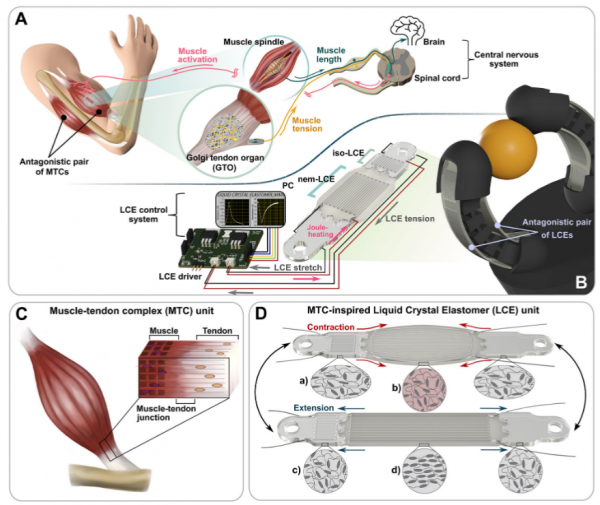
The muscle-tendon complex (MTC) in biological systems integrates contractileactuation and proprioceptive sensing, enabling coordinated feedback control ofmuscle activations through simultaneous afferent (sensory) and efferent (mo-tor) signaling. To achieve similar functionality, artificial muscles, often basedon polymeric materials with intricate material behaviors, require embeddedproprioceptive capabilities to enable adaptive and reliable feedback control.Here, an artificial MTC-inspired liquid crystal elastomer (LCE) muscle withembedded physical intelligence is presented that supports simultaneous sens-ing and actuation. The proposed system utilizes embedded liquid metal (LM)channels for Joule heating and sensing of mechanical states, such as force andlength, within the LCE structure. The multimaterial design combines isotropicLCE and nematic LCE, each with distinct thermomechanical properties opti-mized for specific functions, allowing for responsive contractile actuation andefficient proprioception. Integrated within a single, compact structure, thisartificial muscle combines all sensing and actuation components, enhancingcompliance and proprioceptive functionality. Furthermore, the LCE actuatorsare arranged in an antagonistic pair, mirroring the setup of biological muscles,to improve controllability and coordination. These MTC-inspired LCE artificialmuscles demonstrate closed-loop feedback control in robotic applications,such as a robotic finger and gripper system, highlighting the potentialof embedded physical intelligence in advanced robotic control systems.


